Next: 2 Methodology Description Up: Appnotes Index Previous:Appnote ERED Index
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: 2 Methodology Description
Up: Appnotes Index
Previous:Appnote ERED Index
This document is intended for system engineers and design engineers developing signal processing systems using the RASSP methodology. Though RASSP concentrates mainly in signal processing design its concepts as well as the concepts presented here can be easily extended into the digital systems design environment. It defines how executable requirement specifications are generated and supplied to contractors and bidders for a RASSP project and how conformance to these requirements is established by use of executable design specifications. Contents of executable requirement and design specifications are examined to show the relationships of critical "documentation" components.
The process of distributing of requirements among all project phases from design through manufacturing are covered.
Three significant terms will be used in the text of this Application Note :
Some of these terms have been used previously in the literature and have received somewhat different definitions. To avoid semantic confusion, these terms will have the following meanings in this document :
(The term "written" means text or an equivalent electronic representation of the text material such as a database file set)
Executable Requirement Specification (ER-spec)
Executable Design Specification (ED-spec)
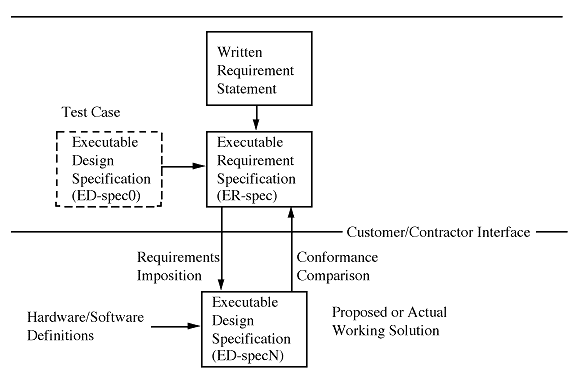
The relationship among these entities is shown in Figure 1 - 1.
The executable requirement specification is always supplemented with the human readable Written Requirement Statement which serves to "comment" the executable requirements in the manner in which "comments" are used in computer programs to explain source code. For this reason, the term executable requirement specification can refer to the combination of the formal ER-spec and a written requirements statement.
The sections below describe the concepts of executable requirements and specifications and their roles in a RASSP project. First a methodology description is presented. Requirements, a rationale for introducing ER-specs into RASSP, and the constituents of executable requirement and design specifications are discussed. Then an examination of the RASSP Benchmark 4 (SAIP) highlighting requirements and defining executable requirements and specifications is performed to illustrate a current attempt at an ER-spec for an ongoing RASSP project.
1.0 Introduction
Projects begin with a statement of requirements which describes values for selected physical properties and how the product must perform. At a minimum, system level requirements are supplied, but requirements that apply at lower packaging levels may also be included. Requirements are used to develop preliminary specifications at the outset of a project and then detailed specifications as the system hardware/software components and human factors evolve. The conventional approach to requirement statement has been a written document. This is typically generated by a customer and interpreted by the contractor. The interpretation process has been shown to be prone to errors. As a consequence, written requirements are being replaced by executable requirements and specifications. This application note describes the contents and usage of these executable elements in a digital systems design environment as developed under the Rapid Prototyping of Application-Specific Signal Processors (RASSP) program. This program relies heavily upon virtual prototyping with VHDL component modeling and simulation.
Written Requirement Statement
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: 2 Methodology Description
Up: Appnotes Index
Previous:Appnote ERED Index